Les Steinmetz - Director of the Americas
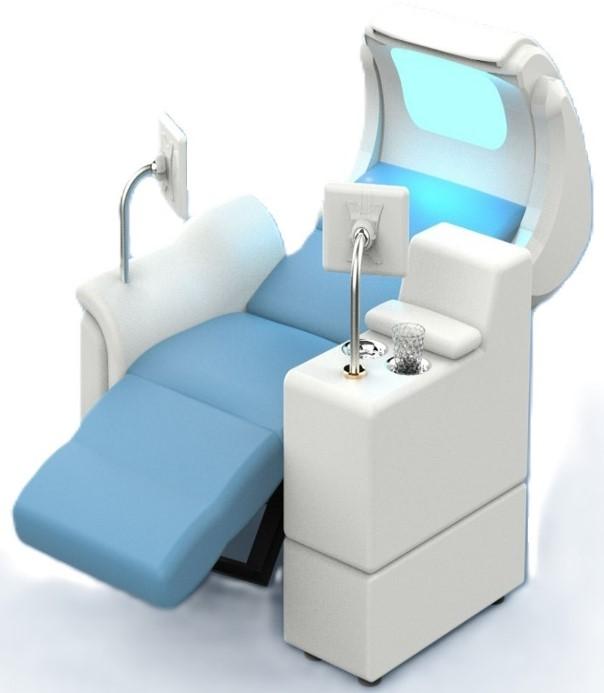
The Svenson Chair
The Svenson Chair is a unique, proprietary medical device which automatically trains the coordination, function and strength of the Pelvic Floor Muscles/related core muscles (Thighs, the muscles of the hipbone area and the glutes). The Chair works by sending magnetic pulses to the patient while he or she is seated, stimulating the autonomic and somatic nerve pathways in the pelvic floor, invigorating the pelvic floor musculature. The Svenson chair is non-invasive, and users enjoy maximum comfort and convenience. Users remain fully clothed during treatments, there is no medical training or specialized personnel required.
Complementary in all indications where Kegel exercises are prescribed.
– Svenson Chair can be used both as a complementary and as a “stand-alone” treatment in treating all indications where Pelvic Floor Muscle exercises (“Kegel” exercises) are prescribed as the first line conservative treatment.
– Kegel exercises have been prescribed by doctors since more than 60 years as the first-line treatment against Urinary Incontinence and various other Pelvic Floor Disorders. Kegel exercises have been proven to be effective in many clinical trials. Not only in relation to Stress Urinary Incontinence but also in relation to many other pelvic floor disorders, including Sexual Function/ Erectile Dysfunction.
– Kegel exercises are effective but there are some inherent issues which make it difficult to carry out the Kegel exercises correctly. Similarly, in relation to lower back pain, it is impossible for a person to train themselves the muscles responsible for spinal segmental stability because these muscles are too deep and too small (i.e. the Multifidus). This is where Svenson Chair, as a complementary treatment, proves its effectiveness.
– Kegel exercises have been prescribed by doctors since more than 60 years as the first-line treatment against Urinary Incontinence and various other Pelvic Floor Disorders. Kegel exercises have been proven to be effective in many clinical trials. Not only in relation to Stress Urinary Incontinence but also in relation to many other pelvic floor disorders, including Sexual Function/ Erectile Dysfunction.
– Kegel exercises are effective but there are some inherent issues which make it difficult to carry out the Kegel exercises correctly. Similarly, in relation to lower back pain, it is impossible for a person to train themselves the muscles responsible for spinal segmental stability because these muscles are too deep and too small (i.e. the Multifidus). This is where Svenson Chair, as a complementary treatment, proves its effectiveness.


Kegel Exercises
Pelvic Floor Muscle exercises are known as “Kegel” exercises.
– Arnold Kegel (American gynecologist):
a. Arnold Kegel popularized in 1948 exercises of the PFM for women to improve sexual and urinary health after childbirth.
b. Arnold Kegel employed the principle of functional restoration of a segregated group of muscles – well established in orthopedics, neuromuscular, and plastic surgery and physical medicine and rehabilitation, applying it to the PFM
c. Arnold Kegel recognized that surgery to correct vaginal, urethral, and rectal
incontinence could be facilitated by preoperative and postoperative PFMT to improve the texture, tone, and function of the perineal muscles.
– Kegel exercises have been proven to be effective in many clinical trials.
Not only in Urinary Incontinence but also in ED
– Arnold Kegel (American gynecologist):
a. Arnold Kegel popularized in 1948 exercises of the PFM for women to improve sexual and urinary health after childbirth.
b. Arnold Kegel employed the principle of functional restoration of a segregated group of muscles – well established in orthopedics, neuromuscular, and plastic surgery and physical medicine and rehabilitation, applying it to the PFM
c. Arnold Kegel recognized that surgery to correct vaginal, urethral, and rectal
incontinence could be facilitated by preoperative and postoperative PFMT to improve the texture, tone, and function of the perineal muscles.
– Kegel exercises have been proven to be effective in many clinical trials.
Not only in Urinary Incontinence but also in ED
Most persons are not able to identify / feel their pelvic floor muscles.
Patients are often not able to feel or identify their Pelvic floor muscles and thus they do not know which muscles they have to train and how.
For that they often need a trained physiotherapist who helps them identifying the right muscles. This is often done in an uncomfortable way (i.e. touching the genital organs). Also the physiotherapist needs to regularly check the patient to ensure he/ she is still carrying out the exercises correctly.
Please note that it is very important to train the right muscles. If patient trains the wrong muscles (i.e. abdominal muscles) then there is a risk that the incontinence issue gets worse rather than improves.
Carrying out Kegel exercises requires daily active commitment
A patient must be willing to do active training every day for 3 times per day for a long period of time. Many patients, especially older patients do not have the energy or time to do this. Often patients start ambitiously with the Kegel training exercises and they are realizing some initial benefits but then after a few months they get disappointed by the low results in relation to the efforts or expectations, and they decide to stop the exercises.
Not easy to intensify the training
As with any type of muscle training, after being able to carry out the exercises at low intensity (which helps with improving the function), the patient must be motivated to strengthen the intensity of the exercises (stronger muscles can only be realized by gradually increasing the intensity of the exercises). With persons doing their own Kegel exercises at home it is very difficult to increase the intensity of the training.
For that they often need a trained physiotherapist who helps them identifying the right muscles. This is often done in an uncomfortable way (i.e. touching the genital organs). Also the physiotherapist needs to regularly check the patient to ensure he/ she is still carrying out the exercises correctly.
Please note that it is very important to train the right muscles. If patient trains the wrong muscles (i.e. abdominal muscles) then there is a risk that the incontinence issue gets worse rather than improves.
Carrying out Kegel exercises requires daily active commitment
A patient must be willing to do active training every day for 3 times per day for a long period of time. Many patients, especially older patients do not have the energy or time to do this. Often patients start ambitiously with the Kegel training exercises and they are realizing some initial benefits but then after a few months they get disappointed by the low results in relation to the efforts or expectations, and they decide to stop the exercises.
Not easy to intensify the training
As with any type of muscle training, after being able to carry out the exercises at low intensity (which helps with improving the function), the patient must be motivated to strengthen the intensity of the exercises (stronger muscles can only be realized by gradually increasing the intensity of the exercises). With persons doing their own Kegel exercises at home it is very difficult to increase the intensity of the training.
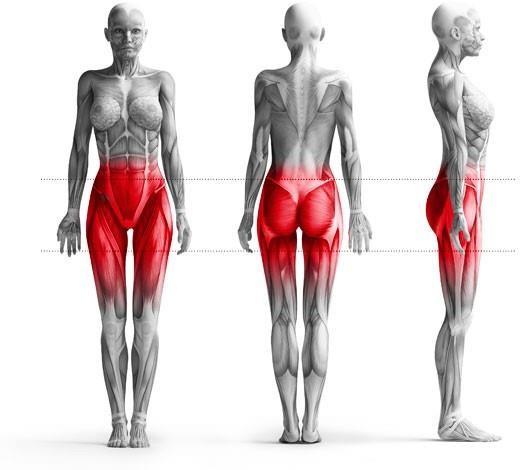
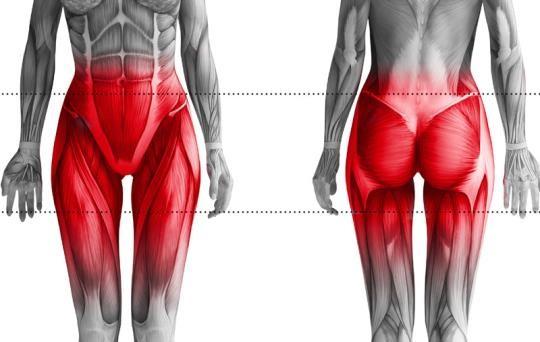
Svenson Chair is automated training of the muscles of the Pelvic Floor and of related muscles such as the thighs, the hip bone and the glutes, and of other “Core” muscles such as the Multifidus & Transversus Abdominis (the last 2 muscles have a very important role in spinal segmental stability and avoiding lower back pain)
Kegel exercises, when carried out correctly, have been proven to be effective by many clinical trials, including Urinary Stress Incontinence and Erectile Dysfunction.
Svenson Chair solves these inherent issues of Kegel exercises and can be used as complementary treatment in all indications where Kegel exercises are prescribed.
Pelvic Floor Muscle Training (PFM) has been known since 1948 as “Kegel exercises” and is the most important conservative (non-surgical) first line treatment in treating many pelvic floor disorders.
However, Kegel exercises (self-exercises) have some inherent issues. As a result of this, it is very difficult to carry out the Kegel exercises correctly.
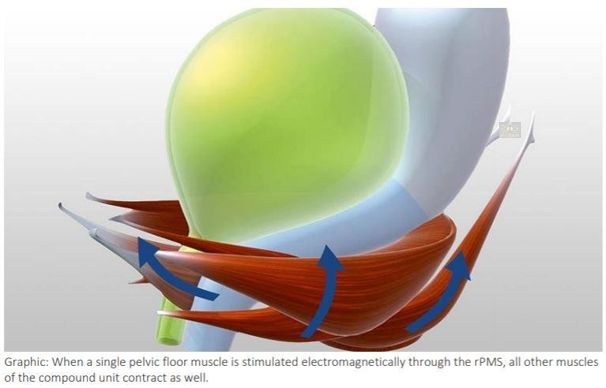
Functionally, the Svenson Chair is using repetitive Peripheral Muscle Stimulation (rPMS) and the repetitive muscle contractions and relaxations results in improved coordination, function, and strength of the Pelvic Floor Muscles.
Svenson Chair has been proven in high quality Clinical Trials.
Kegel exercises, when carried out correctly, have been proven to be effective by many clinical trials, including Urinary Stress Incontinence and Erectile Dysfunction.
Svenson Chair solves these inherent issues of Kegel exercises and can be used as complementary treatment in all indications where Kegel exercises are prescribed.
Pelvic Floor Muscle Training (PFM) has been known since 1948 as “Kegel exercises” and is the most important conservative (non-surgical) first line treatment in treating many pelvic floor disorders.
However, Kegel exercises (self-exercises) have some inherent issues. As a result of this, it is very difficult to carry out the Kegel exercises correctly.
Functionally, the Svenson Chair is using repetitive Peripheral Muscle Stimulation (rPMS) and the repetitive muscle contractions and relaxations results in improved coordination, function, and strength of the Pelvic Floor Muscles.
Svenson Chair has been proven in high quality Clinical Trials.
Muscle Training Introduction:
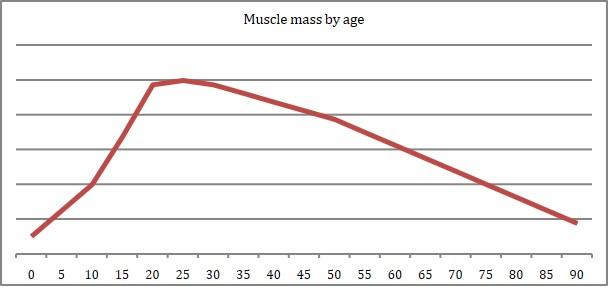
The human body of an adult person consists of about 35%-42% of skeletal muscles.
Muscle mass normally grows until the age of 25 or 30 after which the muscle mass normally starts to decrease with about 1% per year and after the age of 50 even faster. The loss of function and strength of muscles is a key cause for many chronic diseases. In order to maintain function and strength of muscles it is important to regularly use them or train them (“use it or lose it!”)
A Svenson Chair training program follows the key principles of muscle training.
Svenson Chair = Automated Training of Muscles
Muscle mass normally grows until the age of 25 or 30 after which the muscle mass normally starts to decrease with about 1% per year and after the age of 50 even faster. The loss of function and strength of muscles is a key cause for many chronic diseases. In order to maintain function and strength of muscles it is important to regularly use them or train them (“use it or lose it!”)
A Svenson Chair training program follows the key principles of muscle training.
Svenson Chair = Automated Training of Muscles

Key principles of muscle training
Principle of “progressive overload”. Gradually “train” your muscles to handle bigger ‘load’ = higher intensities.
Building strength of muscles can only be realized by high intensity, short duration anaerobic exercises at maximum load.
The principle of “co-contraction”
The principle of “relaxation” which is important after each muscle contraction.
Principle of first focusing on learning to use the muscle before focusing on building strength.
Principle of “warm-up” and “cool-down”.
The principle of training muscles in a concentric, eccentric and isometric way
Building strength of muscles can only be realized by high intensity, short duration anaerobic exercises at maximum load.
The principle of “co-contraction”
The principle of “relaxation” which is important after each muscle contraction.
Principle of first focusing on learning to use the muscle before focusing on building strength.
Principle of “warm-up” and “cool-down”.
The principle of training muscles in a concentric, eccentric and isometric way
Underlying technology of the Svenson Chair
Svenson Chair makes use of the underlying technologies of Q-rPMS and ExMI.
rPMS = Repetitive Peripheral Muscle Stimulation.
ExMI = Extracorporeal Magnetic Innervation.
How does Electromagnetic Stimulation work?
The Svenson Chair produces a highly focused, time-varying magnetic field that penetrates deep into the perineum, stimulating innervation of the pelvic floor muscles by activating all branches of the pudendal and splanchnic nerves, which provokes muscle contraction.
rPMS = Repetitive Peripheral Muscle Stimulation.
ExMI = Extracorporeal Magnetic Innervation.
How does Electromagnetic Stimulation work?
The Svenson Chair produces a highly focused, time-varying magnetic field that penetrates deep into the perineum, stimulating innervation of the pelvic floor muscles by activating all branches of the pudendal and splanchnic nerves, which provokes muscle contraction.

Working of Pulsed Electromagnetic fields in human tissue
High electric currents are applied to a surface stimulation magnetic coil which is integrated in the SVENSON CHAIR.
These electrical currents generate pulsed electro magnetic fields, repetitive, short magnetic field pulses with a duration of 200 to 500 µs and a magnetic flux density of up to 1 Tesla.
At the tissue level, these time varying electro magnetic fields induce electrical eddy currents by an ion flow in the soft tissues of the pelvic floor.
This flow of ions establishes differences in voltage between two spatial points (depolarization of resting motor neurons).
If the voltage gradient is sufficiently strong and the change of field is rapid, membrane depolarization occurs.
This membrane depolarization generates an action potential along adjacent peripheral nerve tissue. The action potential propagates naturally down the axon through the usual Na+ and K+ ion fluxes.
After these impulses reach the motor endplate, the pelvic floor muscle responds by contracting. Unless the output pulse rate exceeds the ability of the muscles to contract and relax, the muscles contract and relax with each pulse.
These electrical currents generate pulsed electro magnetic fields, repetitive, short magnetic field pulses with a duration of 200 to 500 µs and a magnetic flux density of up to 1 Tesla.
At the tissue level, these time varying electro magnetic fields induce electrical eddy currents by an ion flow in the soft tissues of the pelvic floor.
This flow of ions establishes differences in voltage between two spatial points (depolarization of resting motor neurons).
If the voltage gradient is sufficiently strong and the change of field is rapid, membrane depolarization occurs.
This membrane depolarization generates an action potential along adjacent peripheral nerve tissue. The action potential propagates naturally down the axon through the usual Na+ and K+ ion fluxes.
After these impulses reach the motor endplate, the pelvic floor muscle responds by contracting. Unless the output pulse rate exceeds the ability of the muscles to contract and relax, the muscles contract and relax with each pulse.

Impact of Svenson Chair on human tissue and on the Pelvic Floor
Muscle contractions
Magnetic stimulation of peripheral nerves provokes muscle contractions and facilitates the stimulation of autonomic and somatic nerve pathways in the pelvic floor.
Motor evoked potentials are triggered in the pelvic sphincter muscles.
Impact on slow-twitch and fast-twitch fibers.
The Svenson Chair helps the patient to learn how to use certain muscles, resulting in improved function and coordination between the muscles of the Pelvic Floor and increased strength (hypertrophy).
The Svenson Chair trains both the fast-twitch (type II) and the slow-twitch (type I) muscle fibers (via different frequencies and intensities).
Thereby it ensures that PFM are able to respond better to a sudden increase in intra-abdominal pressure.
Also ensures improvement of the resting urethral closure pressure.
Motor evoked potentials are triggered in the pelvic sphincter muscles.
Impact on slow-twitch and fast-twitch fibers.
The Svenson Chair helps the patient to learn how to use certain muscles, resulting in improved function and coordination between the muscles of the Pelvic Floor and increased strength (hypertrophy).
The Svenson Chair trains both the fast-twitch (type II) and the slow-twitch (type I) muscle fibers (via different frequencies and intensities).
Thereby it ensures that PFM are able to respond better to a sudden increase in intra-abdominal pressure.
Also ensures improvement of the resting urethral closure pressure.

Svenson Chair leading to improved Coordination of the PFM
The Pelvic Floor Muscles are a highly complex set of muscles.
For the function of the Pelvic Floor Muscles it is important that the muscles work together in a coordinated manner.
The Svenson Chair does not selectively exercise individual muscles, but affects the entire muscle system of the pelvic floor and muscles in the hip, buttock and thigh region. All important muscles are strengthened at the same time; the muscles that are the weakest due to a lack of activity are strengthened particularly effectively.
This significantly improves the requirements for regaining specific muscle coordination.
As a result of the depolarization of the motor nerves, the extracorporeal magnetic stimulation also causes an intracorporeally generated return flow of proprioceptive data to the brain.
It has been shown that an internal return flow of sensory information, generated through external stimulation, is able to change the cortical representation in the long-term; in addition it is able to improve the personal perception and controllability of individual muscle functions and indirectly also their coordination.
For the function of the Pelvic Floor Muscles it is important that the muscles work together in a coordinated manner.
The Svenson Chair does not selectively exercise individual muscles, but affects the entire muscle system of the pelvic floor and muscles in the hip, buttock and thigh region. All important muscles are strengthened at the same time; the muscles that are the weakest due to a lack of activity are strengthened particularly effectively.
This significantly improves the requirements for regaining specific muscle coordination.
As a result of the depolarization of the motor nerves, the extracorporeal magnetic stimulation also causes an intracorporeally generated return flow of proprioceptive data to the brain.
It has been shown that an internal return flow of sensory information, generated through external stimulation, is able to change the cortical representation in the long-term; in addition it is able to improve the personal perception and controllability of individual muscle functions and indirectly also their coordination.

Old ExMI Technology
Introduction and FDA Approval: Introduced in 1999 in the USA and obtained FDA approval.
Clinical Trials and Acceptance: Despite numerous clinical trials and positive patient testimonials, it was not widely accepted by professional urologists, uro-gynecologists, and physiotherapists.
Limitations: Failed to prove effectiveness in rigorous double-blind randomized controlled trials (RCTs). Specifically, it did not demonstrate statistically significant differences compared to sham treatments.
Outcome: Did not achieve widespread adoption due to lack of robust evidence from high-quality RCTs.
Clinical Trials and Acceptance: Despite numerous clinical trials and positive patient testimonials, it was not widely accepted by professional urologists, uro-gynecologists, and physiotherapists.
Limitations: Failed to prove effectiveness in rigorous double-blind randomized controlled trials (RCTs). Specifically, it did not demonstrate statistically significant differences compared to sham treatments.
Outcome: Did not achieve widespread adoption due to lack of robust evidence from high-quality RCTs.
Svenson Chair’s Enhanced ExMI Technology
Research & Development: Over the last decade, Svenson Chair has invested significantly in research and development, leading to substantial improvements in ExMI technology.
Revolutionized Technology: Resulted in the development of a highly effective and unique treatment approach.
Double Blind RCTs: For the first time, conducted high-quality professional double-blind clinical control trials.
Evidence of Effectiveness: These trials conclusively demonstrate the effectiveness of Magnetic Stimulation in treating Pelvic Floor Disorders, including Stress Urinary Incontinence.
Current Position: Svenson Chair’s technology is now recognized as the most effective non-surgical solution for Stress Urinary Incontinence and other Pelvic Floor Disorders.
Revolutionized Technology: Resulted in the development of a highly effective and unique treatment approach.
Double Blind RCTs: For the first time, conducted high-quality professional double-blind clinical control trials.
Evidence of Effectiveness: These trials conclusively demonstrate the effectiveness of Magnetic Stimulation in treating Pelvic Floor Disorders, including Stress Urinary Incontinence.
Current Position: Svenson Chair’s technology is now recognized as the most effective non-surgical solution for Stress Urinary Incontinence and other Pelvic Floor Disorders.
Proprietary declaration Svenson Chair
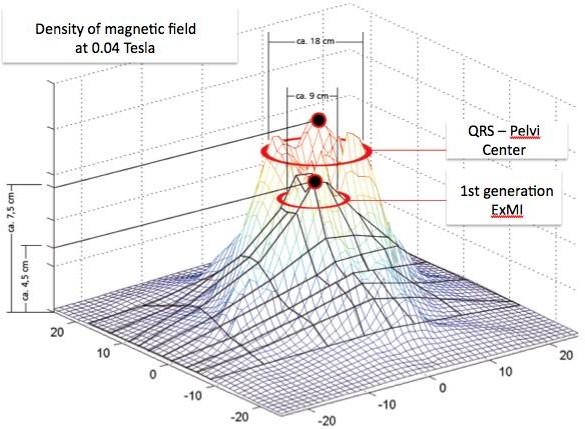
Stronger and Stable Magnetic Field: Svenson Chair features a much stronger and more homogeneous magnetic field, ensuring consistent performance.
4-Arm Magnetic Coil System: Replaces the 2-arm system, enhancing effectiveness and coverage.
Reduced Energy Loss: Minimal energy loss ensures more efficient energy delivery to patients, allowing for longer treatment durations without overheating.
Extended Operating Time: Can operate continuously for over 8 hours per day, compared to older systems requiring cooling down after short sessions.
Longer Pulse Length: Delivers deeper and wider stimulation in the pelvic floor, improving overall effectiveness.
Enhanced Stimulation Coverage: Produces a broader “bell-form” magnetic field, stimulating more muscles and deeper tissues compared to older “knife-form” or “needle-form” fields.
Comprehensive Muscle Activation: Trains all pelvic floor muscles and core muscles including thighs, hips, and glutes, aiding in urinary incontinence treatment and core stability exercises.
Movable Magnetic Coil: Allows precise positioning tailored to patient size and condition, targeting specific pelvic floor muscles effectively.
Ramp-up Functionality: Gradual intensity increase for patient comfort and effectiveness, minimizing abrupt shocks during treatment.
Programmable Chipcard: Enables personalized treatment programs for different indications, ensuring optimal therapy delivery.
High-Quality Clinical Trials: Demonstrated effectiveness in rigorous double-blind RCTs, showing sustained improvements up to 12 months post-treatment compared to sham.
Versatile Treatment Capabilities: Effective for various conditions including Stress Urinary Incontinence, pelvic floor disorders, sexual dysfunction, post-prostatectomy rehabilitation, pregnancy recovery, fecal incontinence, pelvic pain, lower back pain, spinal stability, cellulite, and osteoporosis.
4-Arm Magnetic Coil System: Replaces the 2-arm system, enhancing effectiveness and coverage.
Reduced Energy Loss: Minimal energy loss ensures more efficient energy delivery to patients, allowing for longer treatment durations without overheating.
Extended Operating Time: Can operate continuously for over 8 hours per day, compared to older systems requiring cooling down after short sessions.
Longer Pulse Length: Delivers deeper and wider stimulation in the pelvic floor, improving overall effectiveness.
Enhanced Stimulation Coverage: Produces a broader “bell-form” magnetic field, stimulating more muscles and deeper tissues compared to older “knife-form” or “needle-form” fields.
Comprehensive Muscle Activation: Trains all pelvic floor muscles and core muscles including thighs, hips, and glutes, aiding in urinary incontinence treatment and core stability exercises.
Movable Magnetic Coil: Allows precise positioning tailored to patient size and condition, targeting specific pelvic floor muscles effectively.
Ramp-up Functionality: Gradual intensity increase for patient comfort and effectiveness, minimizing abrupt shocks during treatment.
Programmable Chipcard: Enables personalized treatment programs for different indications, ensuring optimal therapy delivery.
High-Quality Clinical Trials: Demonstrated effectiveness in rigorous double-blind RCTs, showing sustained improvements up to 12 months post-treatment compared to sham.
Versatile Treatment Capabilities: Effective for various conditions including Stress Urinary Incontinence, pelvic floor disorders, sexual dysfunction, post-prostatectomy rehabilitation, pregnancy recovery, fecal incontinence, pelvic pain, lower back pain, spinal stability, cellulite, and osteoporosis.
Summary comparison of Svenson Chair with old ExMI technology
With Svenson Chair you feel real muscle contractions IN the pelvic floor. Important is for doctors to test the Svenson Chair as compared to the older ExMI systems. All doctors who tested the Svenson Chair confirmed that the Svenson Chair has much more power and stimulates the muscles much better. With the Svenson Chair you feel Real Coordinated Muscle Contractions IN the Pelvic Floor and that was not always the case with the previous version of the ExMI technology (with the previous ExMI versions, urologists often concluded that the system was only contracting superficial muscles such as the glutes).
The Svenson Chair / CoreCenter is working on ALL “Core” muscles.
The Svenson Chair / CoreCenter is working on ALL “Core” muscles.
Svenson Chair Pelvic Floor Muscle Training and Stress Urinary Incontinence
Key causes for Stress Urinary Incontinence include
Weakening of urethral sphincters. Total number of skeletal muscle fibers decreases 7 fold as women progress from 15 to 80 years of age (2% per year).
Problems with urethral support. Pelvic floor muscles act as second line of defense in closing the urethra by pushing the urethra against the pubic bone. However, if the pelvic floor muscles are weakened and/or the supporting ligaments/fascia get stretched the pelvic floor muscles are no longer able to support the urinary and reproductive organs and are no longer able to push the urethra against the pubic bone, resulting in incontinence.
Studies Extracorporeal Magnetic Innervation & Stress Urinary Incontinence:
Since 1998 more than 75 studies have been carried out and published. Most of these studies are low quality studies but show that Magnetic Stimulation has positive effects on Stress Urinary Incontinence and Urge Urinary Incontinence. However, the old technology of ExMI has never been able to prove its effectiveness in a double blind Random Clinical Trial. This is also the reason why professional urologists have never accepted the technology. However, SVENSON CHAIR has strongly revolutionized the technology (see other paragraph in this document for a description of the improvements) and SVENSON CHAIR has been carrying out double blind RCTs which have proven, beyond doubt, that Svenson Chair is the most effective non surgical solution against Stress Urinary Incontinence.
Studies Svenson Chair and Stress Urinary Incontinence:
Various high quality studies have been completed. Amongst others in:
Inactive Double Blind Random Clinical Trial (level 1) with 12 month follow-up
India, New Delhi. Study on 90 patients suffering from Stress UI, Urge UI and ED
University of Vienna, Austria. RCT 360 patients from elderly care homes.
Germany: Study by Dr. Zellner focused on Incontinence after Prostatectomy
Various other studies are underway. Please refer to separate paragraph for results of these studies.
Stress Urinary Incontinence and Kegel exercises:
Kegel exercises have been used since the 1950’s in treating Stress Urinary Incontinence with women.
Weakening of urethral sphincters. Total number of skeletal muscle fibers decreases 7 fold as women progress from 15 to 80 years of age (2% per year).
Problems with urethral support. Pelvic floor muscles act as second line of defense in closing the urethra by pushing the urethra against the pubic bone. However, if the pelvic floor muscles are weakened and/or the supporting ligaments/fascia get stretched the pelvic floor muscles are no longer able to support the urinary and reproductive organs and are no longer able to push the urethra against the pubic bone, resulting in incontinence.
Studies Extracorporeal Magnetic Innervation & Stress Urinary Incontinence:
Since 1998 more than 75 studies have been carried out and published. Most of these studies are low quality studies but show that Magnetic Stimulation has positive effects on Stress Urinary Incontinence and Urge Urinary Incontinence. However, the old technology of ExMI has never been able to prove its effectiveness in a double blind Random Clinical Trial. This is also the reason why professional urologists have never accepted the technology. However, SVENSON CHAIR has strongly revolutionized the technology (see other paragraph in this document for a description of the improvements) and SVENSON CHAIR has been carrying out double blind RCTs which have proven, beyond doubt, that Svenson Chair is the most effective non surgical solution against Stress Urinary Incontinence.
Studies Svenson Chair and Stress Urinary Incontinence:
Various high quality studies have been completed. Amongst others in:
Inactive Double Blind Random Clinical Trial (level 1) with 12 month follow-up
India, New Delhi. Study on 90 patients suffering from Stress UI, Urge UI and ED
University of Vienna, Austria. RCT 360 patients from elderly care homes.
Germany: Study by Dr. Zellner focused on Incontinence after Prostatectomy
Various other studies are underway. Please refer to separate paragraph for results of these studies.
Stress Urinary Incontinence and Kegel exercises:
Kegel exercises have been used since the 1950’s in treating Stress Urinary Incontinence with women.
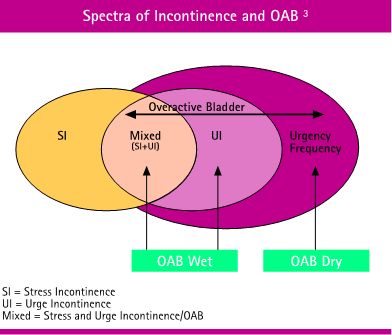
Svenson Chair and Overactive Bladder (OAB)
OAB = Detrusor Instability. OAB has 4 key symptoms:
Urgency: Urgency is the most important symptom of OAB
Definition of urgency: sudden, compelling desire to pass urine which is difficult to defer
O = OAB dry
Frequent urination (but: the amount of urine that is passed when there is an urgent need to urinate is relatively small with OAB)
Frequent interruptions of sleep because of the need to urinate (nocturia)
Urinating unintentionally followed by an urge to continue (urge incontinence)
Involuntary loss of urine occurring for no apparent reason while feeling urinary urgency.
Relationship between OAB, Urgency, and Urge Incontinence:
OAB patients normally have urge but may or may not have leak.
Urge incontinence patients have both urge and leak.
Urgency and Urge Incontinence are symptoms of OAB.
Urgency: Urgency is the most important symptom of OAB
Definition of urgency: sudden, compelling desire to pass urine which is difficult to defer
O = OAB dry
Frequent urination (but: the amount of urine that is passed when there is an urgent need to urinate is relatively small with OAB)
Frequent interruptions of sleep because of the need to urinate (nocturia)
Urinating unintentionally followed by an urge to continue (urge incontinence)
Involuntary loss of urine occurring for no apparent reason while feeling urinary urgency.
Relationship between OAB, Urgency, and Urge Incontinence:
OAB patients normally have urge but may or may not have leak.
Urge incontinence patients have both urge and leak.
Urgency and Urge Incontinence are symptoms of OAB.
Overactive Bladder and Pelvic Floor Muscle Training
The American Urological Association guidelines for OAB recommend that clinicians offer fluid management, bladder training, bladder control strategies, and Pelvic Floor Muscle Training as first-line therapy to all patients with OAB.
Bladder training is focused on training patients to recognize the contractions or the planned contractions of the detrusor muscle (e.g. in the case of hand washing, key in the door; rising from sitting; running water; cold or rainy weather) and to teach the patients to respond by deploying their (skeletal) Pelvic Floor Muscles at the same time. This is the so-called “quick-flick” technique whereby the PFMs are rapidly pulsed 3-5 times at the time when urgency is perceived. Quick rhythmic flicks of the PFM can preempt the involuntary bladder muscles before they contract; or diminish or abort it after urination has begun.
Bladder training is focused on training patients to recognize the contractions or the planned contractions of the detrusor muscle (e.g. in the case of hand washing, key in the door; rising from sitting; running water; cold or rainy weather) and to teach the patients to respond by deploying their (skeletal) Pelvic Floor Muscles at the same time. This is the so-called “quick-flick” technique whereby the PFMs are rapidly pulsed 3-5 times at the time when urgency is perceived. Quick rhythmic flicks of the PFM can preempt the involuntary bladder muscles before they contract; or diminish or abort it after urination has begun.

Effect of Svenson Chair on suppression of involuntary detrusor activity
Activation of hypogastric nerve (activation of inhibitory hypogastric sympathetic neurons).
Stimulates sympathetic fibers, particularly those that maintain smooth muscle tone within the internal sphincter.
Stimulates of the pudendal nerve afferent branches which consequently create an inhibitory spinal reflex through vesico-inhibitory pathways at the S3 nerve root.
Strengthening of the external sphincter which leads indirectly to detrusor relaxation.
Repetitive maximal contraction of the levator muscle complex facilitates the transformation of “fast-twitch” to “slow-twitch” muscle fibers. This reconditioning of the skeletal muscle has a positive indirect effect on Bladder Overactivity.
Stimulates sympathetic fibers, particularly those that maintain smooth muscle tone within the internal sphincter.
Stimulates of the pudendal nerve afferent branches which consequently create an inhibitory spinal reflex through vesico-inhibitory pathways at the S3 nerve root.
Strengthening of the external sphincter which leads indirectly to detrusor relaxation.
Repetitive maximal contraction of the levator muscle complex facilitates the transformation of “fast-twitch” to “slow-twitch” muscle fibers. This reconditioning of the skeletal muscle has a positive indirect effect on Bladder Overactivity.
Overactive Bladder and Urge Urinary Incontinence
Stimulation of the hypogastric plexus (originated in the spinal segment) result in:
Relaxation of the detrusor muscle
Contraction of the internal sphincter, inhibiting urination
Stimulation of the parasympathetic nerves (originating in S2-S4) has the opposite effect:
Contraction of the detrusor muscle
Relaxation of the internal sphincter
Frequency:
Reduction in number of urinary incontinence episodes (voids) as recorded in bladder diary
Severity:
Reduction total score ICIQ-UI-SF
Increase in bladder volume:
Increase in the mean and maximum voided volume per micturition (mL)
Increase in the maximum cystometric capacity (measured by urodynamic study)
Urgency:
Reduction in the number of urgency episodes per 24 hours
Reduction in nocturia
Increase in the Quality of Life (for example measured via the V-8 OAB questionnaire; or the IPSS QOL Index)
Relaxation of the detrusor muscle
Contraction of the internal sphincter, inhibiting urination
Stimulation of the parasympathetic nerves (originating in S2-S4) has the opposite effect:
Contraction of the detrusor muscle
Relaxation of the internal sphincter
Frequency:
Reduction in number of urinary incontinence episodes (voids) as recorded in bladder diary
Severity:
Reduction total score ICIQ-UI-SF
Increase in bladder volume:
Increase in the mean and maximum voided volume per micturition (mL)
Increase in the maximum cystometric capacity (measured by urodynamic study)
Urgency:
Reduction in the number of urgency episodes per 24 hours
Reduction in nocturia
Increase in the Quality of Life (for example measured via the V-8 OAB questionnaire; or the IPSS QOL Index)
Low Back Pain and Spinal Segmental Stability
Svenson Chair is very effective in treating non-specific low back pain, especially when caused by segmental instability. It is more effective than self-training or physiotherapy core stability exercises because segmental stability relies on small, deep muscles like the multifidus and transversus abdominis, which can only be effectively trained with magnetic stimulation.
Lower Back Pain and Functional (Segmental) Stability:
Structural Stability = Passive
Contrary to common belief, there is no relationship between lower back pain and damage to structural stability (vertebrae, facet joints, intervertebral discs, spinal ligaments, joint capsules, passive muscle support).
Without muscles providing functional stability, the spinal cord is unstable.
Functional Stability = Active muscles.
Key stability muscles: transversus abdominus, multifidus, pelvic floor, diaphragm. Lack of movement causes atrophy and loss of “feed-forward” function.
Lumbar instability (L4-L5-S1) in chronic low back pain involves poor movement control. Muscle control equals pain control (White & Panjabi 1990).
Core muscles weaken and lose function without movement, affecting stability and pain management.
Control (Central & Peripheral nervous system)
Lower Back Pain and Functional (Segmental) Stability:
Structural Stability = Passive
Contrary to common belief, there is no relationship between lower back pain and damage to structural stability (vertebrae, facet joints, intervertebral discs, spinal ligaments, joint capsules, passive muscle support).
Without muscles providing functional stability, the spinal cord is unstable.
Functional Stability = Active muscles.
Key stability muscles: transversus abdominus, multifidus, pelvic floor, diaphragm. Lack of movement causes atrophy and loss of “feed-forward” function.
Lumbar instability (L4-L5-S1) in chronic low back pain involves poor movement control. Muscle control equals pain control (White & Panjabi 1990).
Core muscles weaken and lose function without movement, affecting stability and pain management.
Control (Central & Peripheral nervous system)
Lower back pain and “core
stability” exercises:
Physiotherapy
‘Muscle activation’ / ‘ core stability’ exercises
“Core stability” exercises have a positive effect
but inconclusive evidence as to whether “core
stability” exercises are more effective than
normal physical exercise.
Core stability exercises often aren’t more
effective than normal exercises because
training these muscles requires a skilled
physiotherapist
Lower back pain and Pelvic Floor Muscle Exercises:
Studies show a strong link between lower back pain and pelvic floor muscle
dysfunction, stronger than the link with high BMI or inactivity. People with
pelvic floor disorders have a higher risk of lower back pain.
Limited research exists on the effectiveness of pelvic floor muscle training
for lower back pain, but it’s clear that all core muscles are related and must
work together. More research is needed.
The Pelvic Floor is co-active connected to Transversus Abdominus
and Multifidus. Training of the Transversus Abdominus indirectly
trains the pelvic floor. And training of the pelvic floor has a
positive effect on segmental stability (Sapsford et al 2001).
Also, stimulation of thigh muscles has a positive effect also on
other core muscles including “Multifidus” and abdominal muscles.
‘Muscle activation’ / ‘ core stability’ exercises
“Core stability” exercises have a positive effect
but inconclusive evidence as to whether “core
stability” exercises are more effective than
normal physical exercise.
Core stability exercises often aren’t more
effective than normal exercises because
training these muscles requires a skilled
physiotherapist
Lower back pain and Pelvic Floor Muscle Exercises:
Studies show a strong link between lower back pain and pelvic floor muscle
dysfunction, stronger than the link with high BMI or inactivity. People with
pelvic floor disorders have a higher risk of lower back pain.
Limited research exists on the effectiveness of pelvic floor muscle training
for lower back pain, but it’s clear that all core muscles are related and must
work together. More research is needed.
The Pelvic Floor is co-active connected to Transversus Abdominus
and Multifidus. Training of the Transversus Abdominus indirectly
trains the pelvic floor. And training of the pelvic floor has a
positive effect on segmental stability (Sapsford et al 2001).
Also, stimulation of thigh muscles has a positive effect also on
other core muscles including “Multifidus” and abdominal muscles.
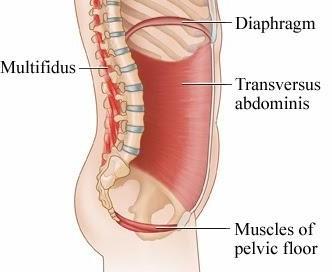
Spinal Segmental Instability is defined as an abnormal response to applied loads, characterized by movement of spinal segments beyond the normal constraints.
Instability of the lumbar spine often occurs in L4-L5 or L5-S1.
Distinction between “global muscles” and “local muscles”:
The Transversus Abdominis and the Lumbar Multifidus are the Primary Stabilizers.
Responsible for spinal stability is not the global (superficial) muscles but the deep small local muscles, in particular the “Multifidus” and the “Transversus Abdominis”.
Instability of the lumbar spine often occurs in L4-L5 or L5-S1.
Distinction between “global muscles” and “local muscles”:
The Transversus Abdominis and the Lumbar Multifidus are the Primary Stabilizers.
Responsible for spinal stability is not the global (superficial) muscles but the deep small local muscles, in particular the “Multifidus” and the “Transversus Abdominis”.

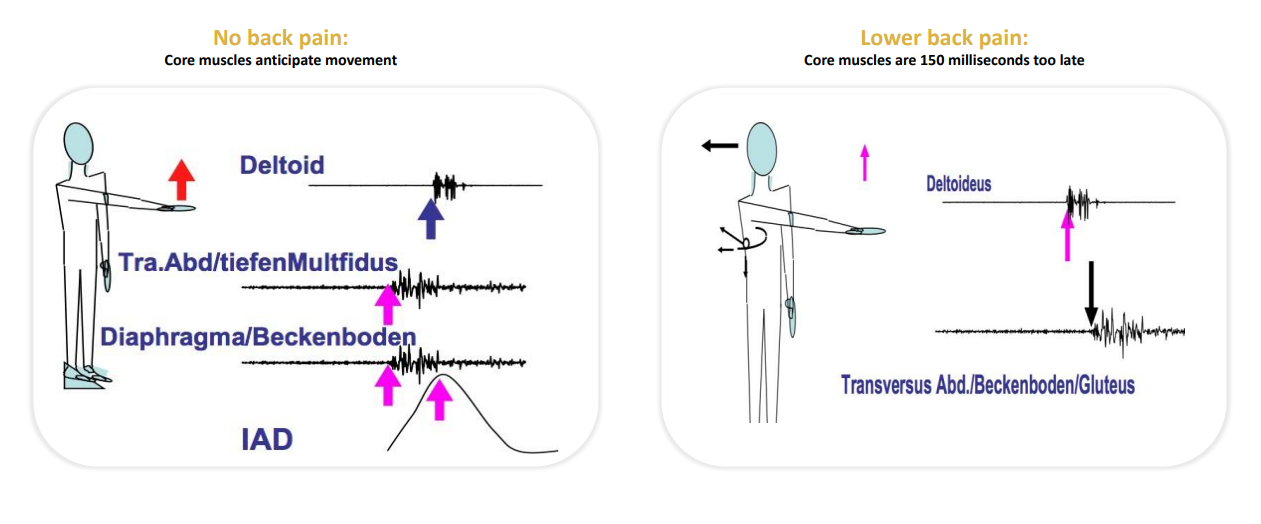
Feed-Forward Mechanism
Svenson Chair and Erectile Dysfunction
Please refer to the separate document “Treatment Protocol Svenson Chair and Erectile Dysfunction & Premature Ejaculation” for a detailed list of all clinical trials. The following are some of the key authors who have done detailed studies into demonstrating the effectiveness of Pelvic Floor Muscle Training on reducing Erectile Dysfunction:
Dorey G et al (UK)
Van Kampen et al (Belgium)
F. Sommer et al (Germany)
The key conclusions of these studies:
There are many potential causes of ED, the most common denominator is blood flow.
The importance of blood flow for sexual function consists of two parts:
Blood must flow into the penis
Blood must stay in the penis and must not flow out too quickly
Various studies in Europe show that between 35% and 60% of patients suffering from ED are suffering from so-called “Venous Occlusive Dysfunction”. This means that their skeletal muscles (ischiocavernosus and bulbospongiosus muscle) are too weak to keep the blood trapped in the penis. The result in increased refractory time, less rigid erections, premature loss of erections, the inability to achieve an erection and reduction in ejaculatory force.
Pelvic Floor Muscle Training and Svenson Chair is especially effective in this group of patients (“venous-occlusive dysfunction”). Please note that Svenson Chair is not “the wonder solution against all ED”. Often a man who suffers from ED has various causes underlying his ED. Svenson Chair helps with one important cause which is called “venous occlusive dysfunction”.
Dorey G et al (UK)
Van Kampen et al (Belgium)
F. Sommer et al (Germany)
The key conclusions of these studies:
There are many potential causes of ED, the most common denominator is blood flow.
The importance of blood flow for sexual function consists of two parts:
Blood must flow into the penis
Blood must stay in the penis and must not flow out too quickly
Various studies in Europe show that between 35% and 60% of patients suffering from ED are suffering from so-called “Venous Occlusive Dysfunction”. This means that their skeletal muscles (ischiocavernosus and bulbospongiosus muscle) are too weak to keep the blood trapped in the penis. The result in increased refractory time, less rigid erections, premature loss of erections, the inability to achieve an erection and reduction in ejaculatory force.
Pelvic Floor Muscle Training and Svenson Chair is especially effective in this group of patients (“venous-occlusive dysfunction”). Please note that Svenson Chair is not “the wonder solution against all ED”. Often a man who suffers from ED has various causes underlying his ED. Svenson Chair helps with one important cause which is called “venous occlusive dysfunction”.
Relevant Pelvic Floor muscles for improvement of sexual function of men and women:
The most important Pelvic Floor Muscles relevant for sexual function are:
Ischiocavernosus muscle
Bulbospongiosus muscle
PC muscle
Ischiocavernosus muscle
Bulbospongiosus muscle
PC muscle
Svenson Chair and Premature Ejaculation
Reduction of force of ejaculation when men get older:
Changes in ejaculatory function are commonly experienced with aging. Ejaculation and orgasm often become less intense, with diminished ejaculatory force and seminal fluid volume.
The bulbospongiosus muscle is responsible for propelling semen after emission. A weakened bulbospongiosus muscle may result in semen dribbling with diminished force or trajectory. A strong bulbospongiosus muscle can generate powerful contractions that can forcibly ejaculate semen at the time of climax.
The stronger the bulbospongiosus muscle, the better the capacity for maximal engorgement of the corpus spongiosum, urethral pressurization, and ejaculation. The intensified ejaculation resulting from a robust bulbospongiosus muscle may enhance the orgasm that accompanies the physical act of ejaculation.
Pelvic floor muscle training may optimize ejaculatory volume, force, and intensity of sexual climax.
About Premature Ejaculation
Premature Ejaculation is the most common male sexual disorder and is a very prevalent condition among urology patients.
Weak pelvic floor muscles make it difficult to delay an ejaculation.
If the patient is able to voluntarily contract the Pelvic Floor Muscles this will help control ejaculation.
See literature overview (appendix to this document). Studies show the effectiveness of Pelvic Floor Muscle training in delaying ejaculation and thus in treating PE.
However, more research is required:
How exactly is the precise mechanism controlling the ejaculatory reflex?
Is control of Premature Ejaculation the result of stronger contracting of the Ischiocavernosus & bulbospongiosus muscle or is it due to relaxation of these muscles?
Changes in ejaculatory function are commonly experienced with aging. Ejaculation and orgasm often become less intense, with diminished ejaculatory force and seminal fluid volume.
The bulbospongiosus muscle is responsible for propelling semen after emission. A weakened bulbospongiosus muscle may result in semen dribbling with diminished force or trajectory. A strong bulbospongiosus muscle can generate powerful contractions that can forcibly ejaculate semen at the time of climax.
The stronger the bulbospongiosus muscle, the better the capacity for maximal engorgement of the corpus spongiosum, urethral pressurization, and ejaculation. The intensified ejaculation resulting from a robust bulbospongiosus muscle may enhance the orgasm that accompanies the physical act of ejaculation.
Pelvic floor muscle training may optimize ejaculatory volume, force, and intensity of sexual climax.
About Premature Ejaculation
Premature Ejaculation is the most common male sexual disorder and is a very prevalent condition among urology patients.
Weak pelvic floor muscles make it difficult to delay an ejaculation.
If the patient is able to voluntarily contract the Pelvic Floor Muscles this will help control ejaculation.
See literature overview (appendix to this document). Studies show the effectiveness of Pelvic Floor Muscle training in delaying ejaculation and thus in treating PE.
However, more research is required:
How exactly is the precise mechanism controlling the ejaculatory reflex?
Is control of Premature Ejaculation the result of stronger contracting of the Ischiocavernosus & bulbospongiosus muscle or is it due to relaxation of these muscles?
Other indications where Svenson chair is helpful as complementary treatment.
Svenson Chair and Pelvic Pain
How is Svenson Chair being able to treat part of CP/CPPS
Pelvic pain has many causes, some still unknown, and may involve pelvic floor dysfunction or neurogenic hypersensitivity/inflammation.
Rapidly changing electromagnetic fields applied noninvasively to the perineum can break the cycle of muscle spasm and neural hypersensitivity/inflammation.
Svenson Chair and Pelvic Floor Muscle training have mixed results but can be effective as complementary treatments for certain pelvic pain cases.
Management of category III CP/CPPS includes various strategies, with Pelvic Floor Muscle Training and Svenson Chair being useful components in some cases.
Pelvic floor muscle training for Pelvic Floor tension Myalgia
Tension myalgia of the levator ani can contribute to chronic prostatitis or chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CP/CPPS), causing pelvic, urogenital, and rectal pain, tightness, spasticity, and affecting sexual, urinary, and bowel function. Neuromuscular dysregulation can be triggered by stress and other factors.
Pelvic Floor Muscle Training (PFMT) helps manage tension myalgia by fostering relaxation of the spastic levator muscle, increasing muscle strength, and promoting relaxation through contraction and relaxation cycles, which is key to managing levator spasticity.
How is Svenson Chair being able to treat part of CP/CPPS
Pelvic pain has many causes, some still unknown, and may involve pelvic floor dysfunction or neurogenic hypersensitivity/inflammation.
Rapidly changing electromagnetic fields applied noninvasively to the perineum can break the cycle of muscle spasm and neural hypersensitivity/inflammation.
Svenson Chair and Pelvic Floor Muscle training have mixed results but can be effective as complementary treatments for certain pelvic pain cases.
Management of category III CP/CPPS includes various strategies, with Pelvic Floor Muscle Training and Svenson Chair being useful components in some cases.
Pelvic floor muscle training for Pelvic Floor tension Myalgia
Tension myalgia of the levator ani can contribute to chronic prostatitis or chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CP/CPPS), causing pelvic, urogenital, and rectal pain, tightness, spasticity, and affecting sexual, urinary, and bowel function. Neuromuscular dysregulation can be triggered by stress and other factors.
Pelvic Floor Muscle Training (PFMT) helps manage tension myalgia by fostering relaxation of the spastic levator muscle, increasing muscle strength, and promoting relaxation through contraction and relaxation cycles, which is key to managing levator spasticity.
What is IC?
A chronic condition in which you experience bladder pressure, bladder pain and sometimes pelvic pain.
With IC the nerve communication between the bladder and the spinal cord via the pelvic nerves gets mixed up, resulting in the patient feeling the need to urinate more often and with smaller volumes of urine than most people.
How effective is Pelvic Floor Muscle Training in treating the symptoms of IC?
75%-80% of IC is related to Pelvic Floor Disorders (Dr. Robert Moldwin USA)
American Urological Association (2010) gave guidelines for treating IC:
1st line of defense includes diet changes and reducing of stress
2nd line of defense includes physiotherapy, medications
(Amitryptilline/ Elmiron) and Bladder installation medications)
With IC the nerve communication between the bladder and the spinal cord via the pelvic nerves gets mixed up, resulting in the patient feeling the need to urinate more often and with smaller volumes of urine than most people.
How effective is Pelvic Floor Muscle Training in treating the symptoms of IC?
75%-80% of IC is related to Pelvic Floor Disorders (Dr. Robert Moldwin USA)
American Urological Association (2010) gave guidelines for treating IC:
1st line of defense includes diet changes and reducing of stress
2nd line of defense includes physiotherapy, medications
(Amitryptilline/ Elmiron) and Bladder installation medications)

Svenson Chair and Premature Ejaculation
Standard treatment program Svenson Chair and Faecal Incontinence:
Complementary treatment
Svenson Chair is effective as a complementary treatment in treating Faecal Incontinence.
Intensity:
The key focus is building strength. Ideal program is to use 35 Herz.
Some notes about Stool:
The EAS (External Anal Sphincter) is designed to hold back solid and not so well suited to hold back loose stool.
Measurement before:
Test the strength and endurance via direct digital muscle assessment.
Number of sessions:
Recommendation is to do 16 treatments of progressive intensity and strengthening.
Dietary advise:
Dietary advise to reduce inflammation/irritation.
Position the coil:
Focus on the Anal Sphincter. Normally about 0-2 cm for women. And 3 cm for men.
Some attention points:
Be careful when treating patients with anal fissure or hemorrhoids. MEbo repair ointment is natural.
Complementary treatment
Svenson Chair is effective as a complementary treatment in treating Faecal Incontinence.
Intensity:
The key focus is building strength. Ideal program is to use 35 Herz.
Some notes about Stool:
The EAS (External Anal Sphincter) is designed to hold back solid and not so well suited to hold back loose stool.
Measurement before:
Test the strength and endurance via direct digital muscle assessment.
Number of sessions:
Recommendation is to do 16 treatments of progressive intensity and strengthening.
Dietary advise:
Dietary advise to reduce inflammation/irritation.
Position the coil:
Focus on the Anal Sphincter. Normally about 0-2 cm for women. And 3 cm for men.
Some attention points:
Be careful when treating patients with anal fissure or hemorrhoids. MEbo repair ointment is natural.
Svenson Chair and reduction of Cellulite
Svenson Chair, when used as a complementary treatment, can have a positive effect on tightening the buttocks/glutes and reducing cellulite.
Standards treatment program Svenson Chair and Cellulite:
Normally a customer takes a course of 16 treatments. The standard rule when using Svenson Chair (for example for Urinary Incontinence) is that the customer can do maximum 1 treatment of 20 minutes per day.
A typical treatment plan the customer is normally provided 2 treatments of 20 minutes in 1 hour. However the position of the magnetic coil is different in each of the 2 sessions, so for example:
Standards treatment program Svenson Chair and Cellulite:
Normally a customer takes a course of 16 treatments. The standard rule when using Svenson Chair (for example for Urinary Incontinence) is that the customer can do maximum 1 treatment of 20 minutes per day.
A typical treatment plan the customer is normally provided 2 treatments of 20 minutes in 1 hour. However the position of the magnetic coil is different in each of the 2 sessions, so for example:

Differences between Svenson Chair and Electric Stimulation
Electrical stimulation directly stimulates the nerves. Magnetic stimulation generates an ion flow and eddy currents to which nerve tissue is particularly sensitive.
Spatial distribution of the Magnetic field is larger and has the space of a hollow “dough-nut” in contrast to the limited “bull’s eye” field that is created by electrical stimulation.
Most importantly, a magnetic field is unaffected by tissue impedance and can thereby reach deeper into the Pelvic Floor. Electrical stimulation requires relatively high voltages at the skin compensate for decay as the current traverses soft tissue and bone.
Electrical stimulation is more painful and some clinical tests show that with electrical stimulation the episodes of incontinence can increase rather than decrease.
Spatial distribution of the Magnetic field is larger and has the space of a hollow “dough-nut” in contrast to the limited “bull’s eye” field that is created by electrical stimulation.
Most importantly, a magnetic field is unaffected by tissue impedance and can thereby reach deeper into the Pelvic Floor. Electrical stimulation requires relatively high voltages at the skin compensate for decay as the current traverses soft tissue and bone.
Electrical stimulation is more painful and some clinical tests show that with electrical stimulation the episodes of incontinence can increase rather than decrease.
Summary key points when doing a treatment with Svenson Chair:
Always first check the contra-indications.
Determine the indication:
For Urge Incontinence: 10 Hz or 5 Hz; for Stress Incontinence: 35-50 Hz, but at 80-100% intensity, stick to 35 Hz to prevent muscle fatigue and soreness, despite 50 Hz being theoretically better for strength.
Long term results:
It is important to complete the full program (normally 16 treatments). Patients can stop earlier if they want but in that case, we can not guarantee long term results.
Start first treatment at low intensity and low frequency.
Motivate the customer to gradually increase the intensity from 20% to 100% over 6-10 sessions to improve muscle coordination and function, ensuring no pain is felt.
Lower Back Pain: Focus the stimulation on 2 parts:
Pelvic floor muscles and thigh muscles (15 minutes)
Direct stimulation of the lower back (multifidus) (15 minutes)
Notes:
Always vary the magnetic coil position for each patient (based on body type) and each indication (e.g., lower back pain, fecal incontinence, stress incontinence, sexual function) to ensure optimal benefit from Svenson Chair treatment.
Determine the indication:
For Urge Incontinence: 10 Hz or 5 Hz; for Stress Incontinence: 35-50 Hz, but at 80-100% intensity, stick to 35 Hz to prevent muscle fatigue and soreness, despite 50 Hz being theoretically better for strength.
Long term results:
It is important to complete the full program (normally 16 treatments). Patients can stop earlier if they want but in that case, we can not guarantee long term results.
Start first treatment at low intensity and low frequency.
Motivate the customer to gradually increase the intensity from 20% to 100% over 6-10 sessions to improve muscle coordination and function, ensuring no pain is felt.
Lower Back Pain: Focus the stimulation on 2 parts:
Pelvic floor muscles and thigh muscles (15 minutes)
Direct stimulation of the lower back (multifidus) (15 minutes)
Notes:
Always vary the magnetic coil position for each patient (based on body type) and each indication (e.g., lower back pain, fecal incontinence, stress incontinence, sexual function) to ensure optimal benefit from Svenson Chair treatment.
Additional notes from SVENSON CHAIR – Corporate Head Office
Notes on how Svenson Chair works
The magnetic field penetrates cellular tissue without resistance.
The pulsating magnetic fields target the motor nerves and induces them to transmit electrical current to the muscle fibers with the neuromuscular junction.
At a threshold, Action Potentials in motor nerves cause involuntary contractions. Svenson Chair stimulates these nerves, causing contractions at low (e.g., 5 Hz) or high (e.g., 50 Hz) frequencies.
Mechanoreceptors detect rPMS and send signals to the CNS, creating new neural connections for better pelvic floor muscle control.
During rPMS therapies, the CNS learns to control the treated muscle area, enhancing muscle control over time.
The magnetic field penetrates cellular tissue without resistance.
The pulsating magnetic fields target the motor nerves and induces them to transmit electrical current to the muscle fibers with the neuromuscular junction.
At a threshold, Action Potentials in motor nerves cause involuntary contractions. Svenson Chair stimulates these nerves, causing contractions at low (e.g., 5 Hz) or high (e.g., 50 Hz) frequencies.
Mechanoreceptors detect rPMS and send signals to the CNS, creating new neural connections for better pelvic floor muscle control.
During rPMS therapies, the CNS learns to control the treated muscle area, enhancing muscle control over time.
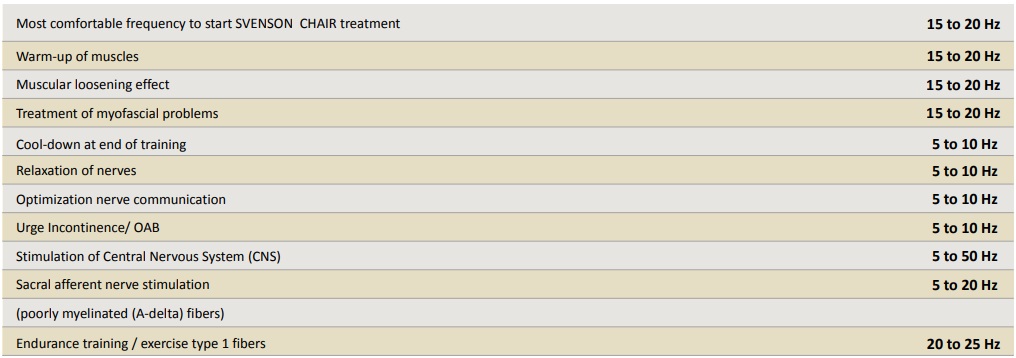
Treatment Protocol Various Indications
The following recommendations for therapeutic stimulation configurations are based on studies, experience and the basic principles of strength training. We suggest that you adhere to the recommended settings as far as possible.
Please note that High Frequencies work better for training fast twitch, type 2 muscles (which is for example important for training the external sphincter muscle for ensuring closure of the urethra to prevent against urinary incontinence).
Values from 20 to 25 Hz correspond to the threshold stimulation (the fused contraction frequency) at which slow-twitch type I muscle fibres contract to produce tetanic muscle contractions.
Please note that High Frequencies work better for training fast twitch, type 2 muscles (which is for example important for training the external sphincter muscle for ensuring closure of the urethra to prevent against urinary incontinence).
Values from 20 to 25 Hz correspond to the threshold stimulation (the fused contraction frequency) at which slow-twitch type I muscle fibres contract to produce tetanic muscle contractions.
Postpartum Training
Postpartum rPMS training requires the use of different stimulus configurations which should be determined by considering the complexity of delivery sequelae and the period of time elapsed since delivery (stress urinary incontinence and/or faecal incontinence, genital prolapse, pelvic pain syndrome, dyspareunia, etc.) If, for example, birth-related nerve damage is suspected, which often remains untreated, stimulation of the pudendal nerve or pro-regenerative BDNF (brain-derived neurotrophic factor) cytokine stimulation should be started as early as possible. The general objective is not so much a rapid “healing” of postpartum urinary or faecal incontinence or an immediate relief of pain, but rather an acceleration of the body’s own repair processes in order to prevent the development of chronic conditions or a deterioration of potential trauma sustained during delivery.
Postpartum – Pudendal nerve rehabilitation/BDNF stimulation
Start: As early as possible or in line with the wound healing process following episiotomy. Even if longer application times (e.g. 40 minutes) would be optimal for the activation of BDNF growth factor synthesis, significant BDNF synthesis can still be achieved using shorter treatment times.
Postpartum – Urinary and faecal incontinence, anal flatus symptoms, organ prolapse
Only start treatment after completion of the entire BDNF stimulation schedule. Stimulation configurations are based on SUI application principles.
Postpartum – Pudendal nerve rehabilitation/BDNF stimulation
Start: As early as possible or in line with the wound healing process following episiotomy. Even if longer application times (e.g. 40 minutes) would be optimal for the activation of BDNF growth factor synthesis, significant BDNF synthesis can still be achieved using shorter treatment times.
Postpartum – Urinary and faecal incontinence, anal flatus symptoms, organ prolapse
Only start treatment after completion of the entire BDNF stimulation schedule. Stimulation configurations are based on SUI application principles.
Stress Urinary Incontinence – Women and Men
Since there is an inverse relationship between type II fibre content and muscle strength, it is not the endurance or type I fibres that are preferentially exercised, but rather the fast-twitch muscle fibres. Since the physiologic tetanus threshold of type I fibres is lower, these fibres cannot be isolated and are therefore also exercised. Stimulation should preferably focus on the anterior portions of the pelvic floor, although medium and posterior portions of the pelvic floor can also be exercised for short periods of time on account of rapid muscle fatigue.
Stress Urinary Incontinence for women often happens after Pregnancy.
Also SUI for women often happens after Menopause.
Stress Urinary Incontinence for women often happens after Pregnancy.
Also SUI for women often happens after Menopause.
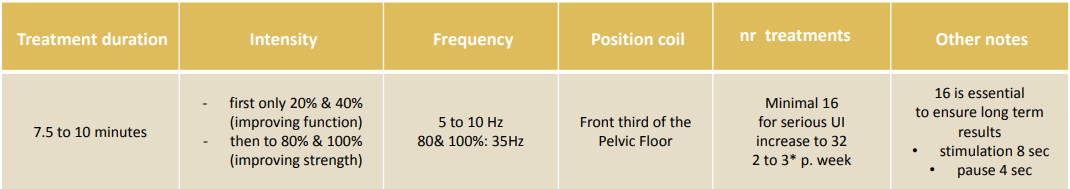
Maintenance program for Stress Urinary Incontinence
For everybody who is suffering from SUI after menopause, we recommend first to do a full “Rehabilitation program” by using Svenson Chair at least 16 times.
After the “rehabilitation”, despite the fact that Studies have proven that Svenson Chair has a long term positive effect, still we recommend that you follow a “Maintenance Program” after that. We recommend a maintenance program of 2 treatments per month (24 treatments per year).
Note that such a maintenance program is normally not so important for younger women (e.g. who suffered of SUI after pregnancy/child birth) because for them they will most likely on a daily basis restart using their pelvic floor muscles and thereby do not need so much the special Svenson Chair treatment for maintenance.
After the “rehabilitation”, despite the fact that Studies have proven that Svenson Chair has a long term positive effect, still we recommend that you follow a “Maintenance Program” after that. We recommend a maintenance program of 2 treatments per month (24 treatments per year).
Note that such a maintenance program is normally not so important for younger women (e.g. who suffered of SUI after pregnancy/child birth) because for them they will most likely on a daily basis restart using their pelvic floor muscles and thereby do not need so much the special Svenson Chair treatment for maintenance.

Urge Urinary Incontinence (UUI) and Overactive Bladder (OAB)
UUI & OAB women
rPMS for urge urinary incontinence (UUI) focuses on treating detrusor hyperactivity. There are two possible target options:
Activation of somato-sensitive fibres of the pudendal nerve, which can block the spinal cord neurological “gate”. This is used to prevent the transmission of chaotic afferent signals to the CNS (e.g. neuromodulation).
Exercising a potentially excessively weak pelvic floor. The purpose of this is to help lift a prolapsed bladder caused by a structural anomaly of the pelvic floor. The stimulation ratio for this should be about 6:4.
UUI & OAB men
The male UUI differs from the female version insofar as a potential impact of an excessively weak pelvic floor is of little relevance in men.
rPMS for urge urinary incontinence (UUI) focuses on treating detrusor hyperactivity. There are two possible target options:
Activation of somato-sensitive fibres of the pudendal nerve, which can block the spinal cord neurological “gate”. This is used to prevent the transmission of chaotic afferent signals to the CNS (e.g. neuromodulation).
Exercising a potentially excessively weak pelvic floor. The purpose of this is to help lift a prolapsed bladder caused by a structural anomaly of the pelvic floor. The stimulation ratio for this should be about 6:4.
UUI & OAB men
The male UUI differs from the female version insofar as a potential impact of an excessively weak pelvic floor is of little relevance in men.
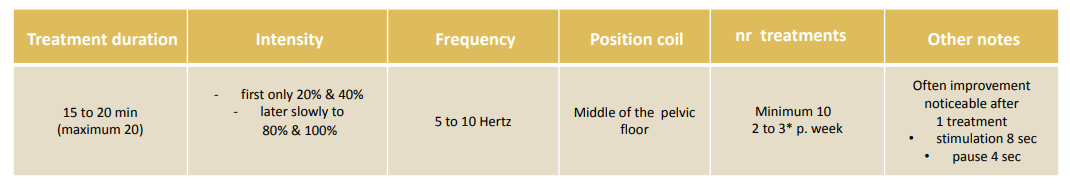
Mixed Urinary Incontinence (MUI)
With this form of incontinence, which is common in advanced age, the duration of application is dependent on the prevalence of symptoms (urge or stress incontinence). The frequency setting here is based on two different forms of incontinence, i.e. during a single treatment session of 20 minutes, the OAB/UUI is treated with 5 to 10 Hz and subsequently the SUI with 50 Hz.
In men with mixed incontinence, the urge urinary incontinence (UUI) component is more pronounced. This is why it is important to note that therapy should also be initiated with a number of mixed settings. We therefore recommend two different stimulus configurations, each used alternately on day 1 and day 2:
Day 1: OAB/urge incontinence
Day 2: Stress urinary incontinence
In men with mixed incontinence, the urge urinary incontinence (UUI) component is more pronounced. This is why it is important to note that therapy should also be initiated with a number of mixed settings. We therefore recommend two different stimulus configurations, each used alternately on day 1 and day 2:
Day 1: OAB/urge incontinence
Day 2: Stress urinary incontinence
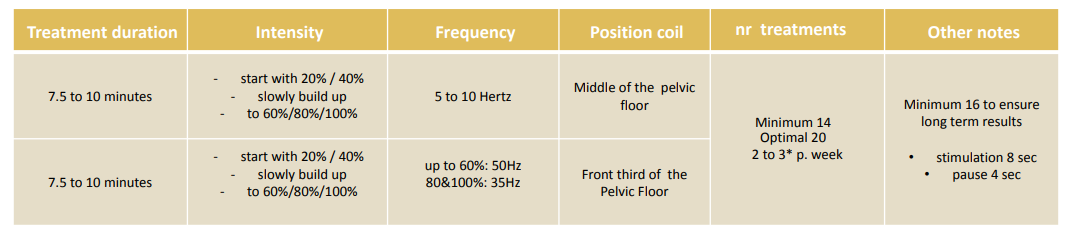
Sexual Function (men & women)
Penile, i.e. atherosclerotic or age-related blood influx disorders usually lead to cavernous fibrosis, which in the case of erection results in insufficient filling of cavernous bodies and a venous leak. The target region of an rPMS in these cases is the ischiocavernosus muscle, which with powerful contractions provides effective emissary vein closure and increased penile blood filling pressures. Penile fibrosis also responds well to rPMS treatment, as an improvement in microcirculation can alter the imbalance between connective tissue and smooth muscle cells in favour of smooth muscles.
NOTE: Longer treatment times (> 8 months) must be planned for these cases.
NOTE: Longer treatment times (> 8 months) must be planned for these cases.
Sexual Function (men & women)
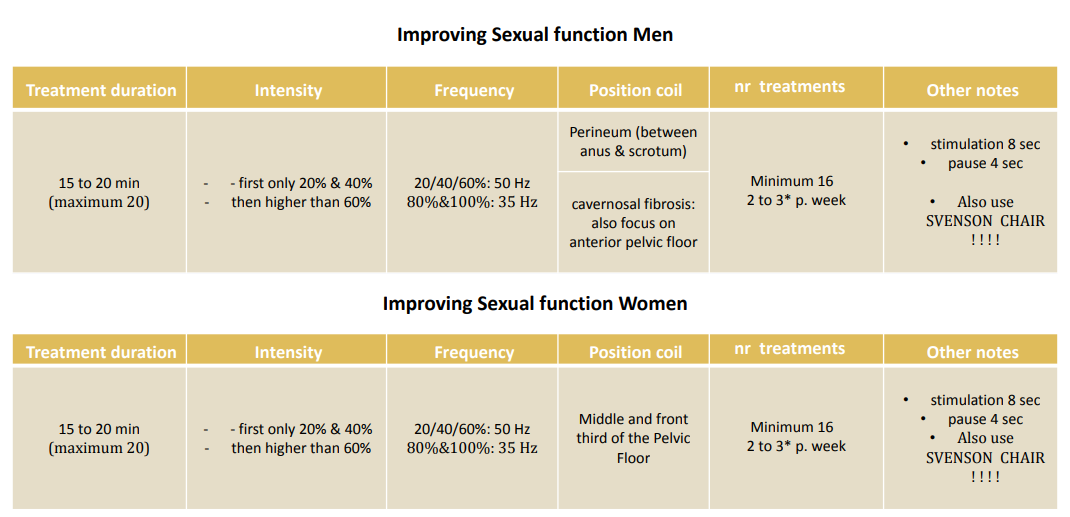
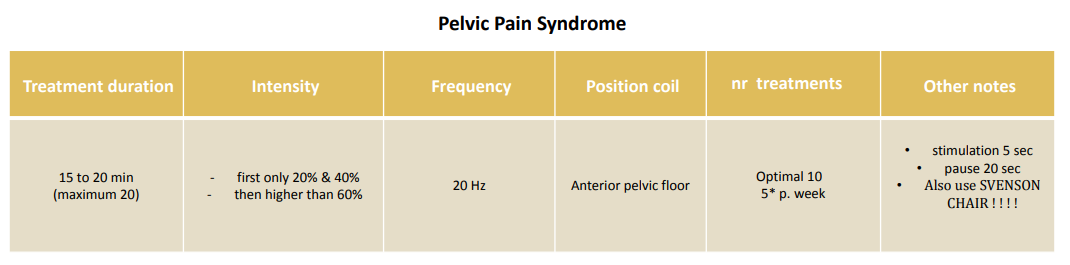
Pelvic Pain syndrome (PPs)/ peritrochanteric pain syndrome (coxarthrosis)
For myofascial pain syndrome (trigger points/formation of muscle knots), which characterises PPS, the intensity of rPMS is determined based on the degree of pain the patient can tolerate and can therefore already be increased from 20% intensity (step 1) to step 3 or 4 in the first session. The stimulation and pause times also differ compared to those used to treat urinary incontinence. Depending on the severity and chronic character of the disease, beneficial effects can already be felt after a single session. In order to promote long-term effects, however, the treatment series provided for this purpose should be fully exploited.
Find Us – Rebirth USA
Contact
Director of the Americas
Les Steinmetz
Our Phone: (310) 874-1300
Our Website: www.Rebirthglobe.com
Our Email: [email protected]
Director of the Americas
Les Steinmetz
Our Phone: (310) 874-1300
Our Website: www.Rebirthglobe.com
Our Email: [email protected]

